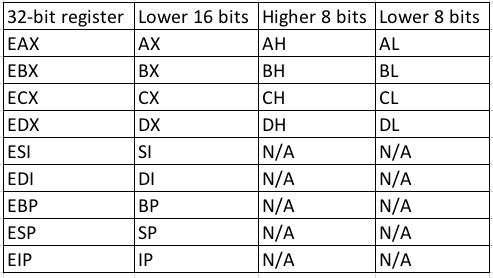
General Purpose Registers
- EAX (accumulator): Arithmetical and logical instructions, function return value
- EBX (base): Base pointer for memory addresses
- ECX (counter): Loop, shift, and rotation counter
- EDX (data): I/O port addressing, multiplication, and division
- ESI (source index): Pointer addressing of data and source in string copy operations
- EDI (destination index): Pointer addressing of data and destination in string copy operations
Special Registers
- EBP (base pointer): points to the start of the current stack frame, i.e. the return address; arguments and local variables are accessed EBP address offsets (i.e.
ebp + 0x04). - ESP (stack pointer): points to the top of the stack (latest data pushed onto the stack)
- EIP (instruction pointer): points to the next instruction; one of the primary target for exploiting a memory-related vulnerability such as a buffer overflow.
Each CPU manufacturer may have their own special registers (like control registers).